What is Myocardial Infarction?
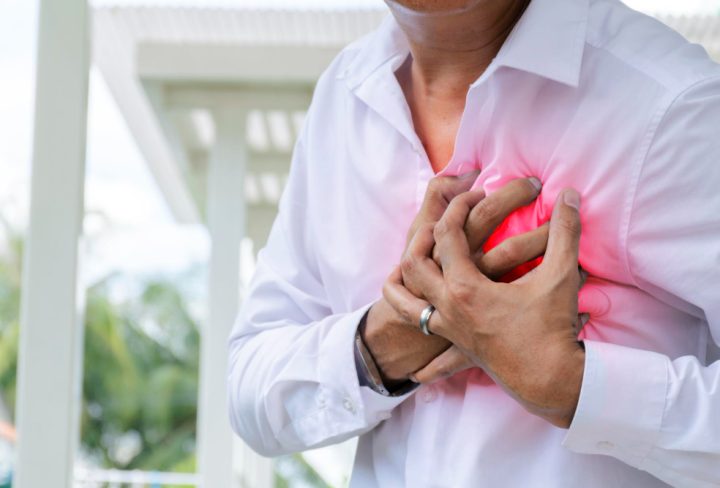
Myocardial infarction, often called a heart attack, is a serious medical emergency. It happens when blood flow to part of the heart muscle stops. As a result, the heart muscle does not get enough oxygen. This can cause lasting damage if not treated quickly. In the United States, heart attacks are a leading cause of death, according to the CDC. Early recognition and treatment can save lives and improve heart health.
Common Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of myocardial infarction is important. Early action can make a big difference. While symptoms may vary, some are more common than others. For example, chest pain is the most frequent sign. However, not everyone feels the same symptoms.
Sometimes, symptoms can be mild or mistaken for indigestion. Women, older adults, and people with diabetes may have less typical signs. Therefore, it is important to seek emergency care if you notice any warning signs.
Leading Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of myocardial infarction. Most heart attacks happen because of blocked arteries. These blockages are often caused by a buildup of fat, cholesterol, and other substances. This buildup is called plaque.
Because some risk factors can be controlled, making healthy choices can lower your risk. However, some factors, like age and family history, cannot be changed.
Diagnosis Methods
Doctors use several methods to diagnose myocardial infarction. Quick diagnosis helps start treatment early. First, a doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history. Then, they will perform a physical exam. Next, tests are used to confirm a heart attack.
Because time is critical, these tests are often done quickly in the emergency room.
Treatment Options
Treatment for myocardial infarction aims to restore blood flow and limit heart damage. Both non-interventional and interventional cardiology approaches are used. The choice depends on the type and severity of the heart attack.
Non-Interventional Treatments
Doctors may use these treatments if the blockage is small or if a procedure is not possible right away.
Interventional Treatments
Because these procedures restore blood flow quickly, they are often used in emergency care.
Lifestyle Tips for Recovery
After a heart attack, making healthy changes is important for recovery. These steps can help your heart heal and lower the risk of another cardiac event.
Because recovery takes time, be patient with yourself and ask for support when needed.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing myocardial infarction is possible for many people. Simple changes can protect your heart and improve your overall health. For example, regular check-ups help catch problems early.
Because some risk factors are out of your control, talk to your doctor about your personal risk. The CDC and WHO both recommend regular screenings for heart health.
If you or someone you know experiences symptoms of a heart attack, seek emergency medical care immediately. Consult a cardiologist for personalized advice.