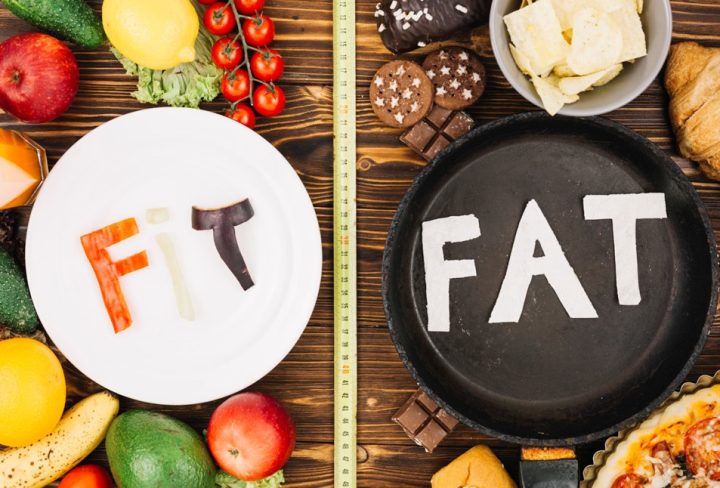
Dyslipidemia refers to an abnormal concentration of lipids in the blood, including cholesterol and triglycerides. High levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or “bad” cholesterol and low levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) or “good” cholesterol can lead to the formation of plaques in the arteries, which can cause them to narrow and harden. This can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases.
Causes of Dyslipidemia
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of dyslipidemia, including:
- Genetics
- Obesity
- Unhealthy diet
- Lack of physical activity
- Diabetes
- Hypothyroidism
- Liver or kidney disease
Symptoms of Dyslipidemia
Dyslipidemia usually does not cause any symptoms until it has progressed to a more advanced stage. In some cases, people may experience symptoms such as:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Numbness or weakness in the limbs
Diagnosis of Dyslipidemia
Dyslipidemia can be diagnosed through a blood test that measures the levels of various lipids in the blood. The American Heart Association recommends that adults get their cholesterol levels checked every four to six years, starting at age 20.
Treatment of Dyslipidemia
Treatment of dyslipidemia usually involves lifestyle changes and medication. Lifestyle changes may include:
- Medications
- Eating a healthy diet
- Exercising regularly
- Losing weight
- Quitting smoking
- Limiting alcohol consumption
Conclusion
Dyslipidemia is a common condition that can increase the risk of developing heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases. It can be managed through lifestyle changes and medication. Regular cholesterol screening is important in identifying and treating dyslipidemia. If you have any concerns about your cholesterol levels, talk to your healthcare provider.