Introduction
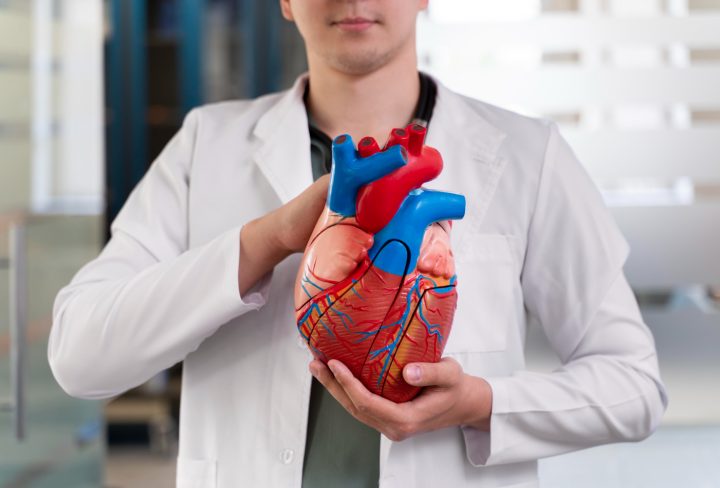
Rheumatic valvular disease is a heart condition that affects the heart valves. It often develops after rheumatic fever, which can follow untreated strep throat. Because this disease can cause lasting heart valve damage, it is important to know its signs and how to manage it. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), rheumatic heart disease remains a major health problem in many countries. Early care can help prevent serious complications.
Symptoms
Symptoms of rheumatic valvular disease may not appear right away. However, as the condition worsens, you may notice:
Sometimes, symptoms of rheumatic heart disease can be mild at first. But over time, they may get worse if not treated.
Causes and Risk Factors
Rheumatic valvular disease usually starts with rheumatic fever. This fever is a reaction to a strep throat infection that was not treated properly. The body’s immune system attacks its own tissues, including the heart valves. Over time, this can lead to heart valve damage from rheumatic fever.
Several factors increase the risk:
Children between ages 5 and 15 are most at risk. However, adults can also develop this disease if they had rheumatic fever as children.
Diagnosis
Doctors use several tests to diagnose rheumatic valvular disease. First, they will ask about your symptoms and medical history. Next, they may listen to your heart with a stethoscope for unusual sounds called murmurs.
Common tests and procedures include:
Early diagnosis helps prevent further heart damage and guides the best treatment for rheumatic valve problems.
Treatment Options
Treatment for rheumatic valvular disease depends on how severe the valve damage is. Doctors may suggest:
With the right treatment, many people can live active lives. However, ongoing care is important to prevent problems.
Lifestyle Guidance and Prevention
There are steps you can take to protect your heart and prevent rheumatic valvular disease:
Additionally, good hygiene and clean living conditions can help prevent strep infections. Early treatment of sore throats in children is key.
When to See a Doctor
If you notice symptoms like shortness of breath, chest pain, or swelling, see a doctor right away. Also, if you had rheumatic fever in the past, regular heart check-ups are important. Early care can prevent serious heart problems later on.
Conclusion
Rheumatic valvular disease can cause lasting heart valve damage if not treated. But with early diagnosis and the right care, you can manage symptoms and protect your heart. Consult a cardiologist for personalized guidance.